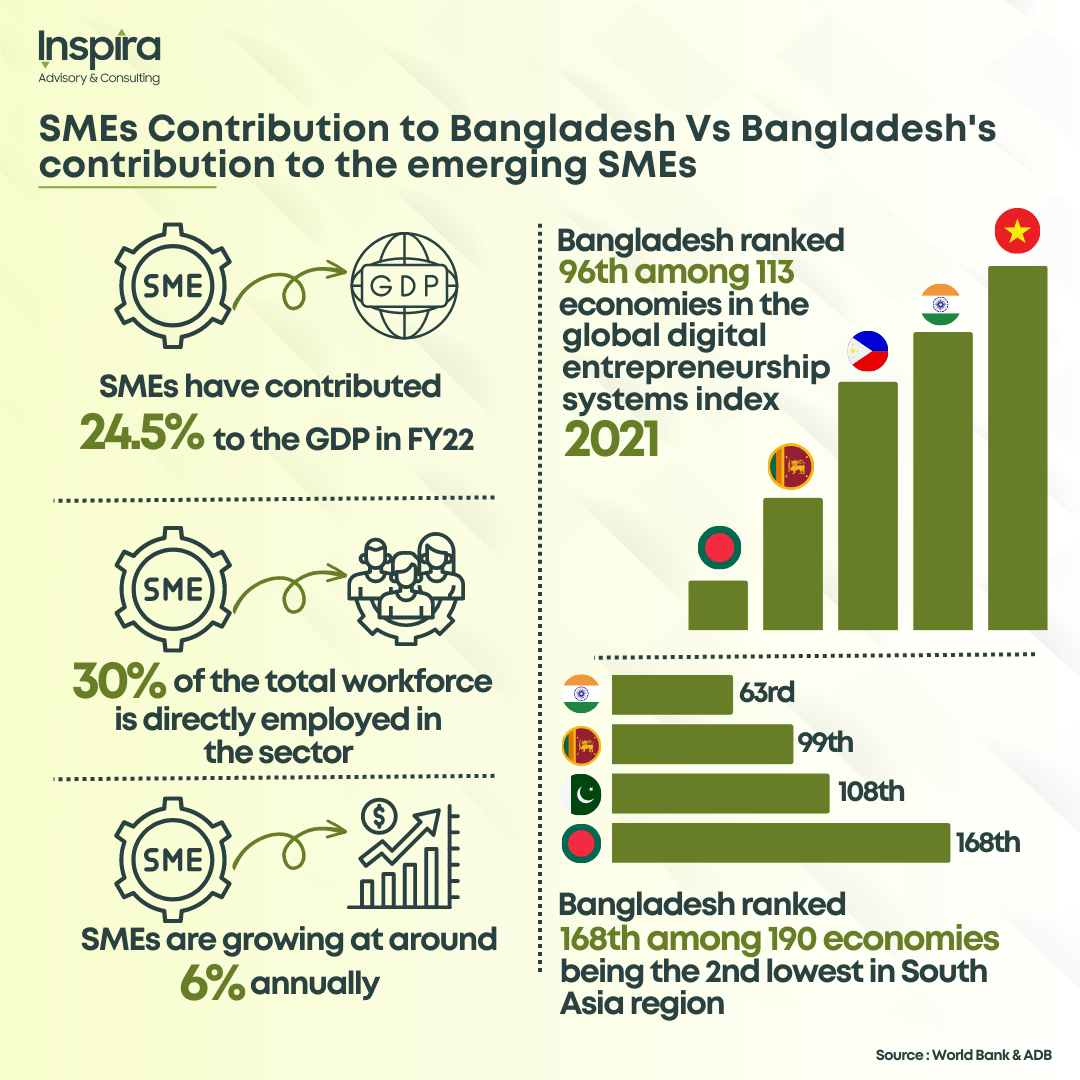
As Bangladesh strides towards the 4th Industrial Revolution (4IR), our economy experiences significant growth across various sectors, including IT services and healthcare. Despite boasting 7.8 million SME entrepreneurs and a consistent contribution to GDP growth from 20% in FY17 to 24.5% in FY22, the country ranks 18th from the bottom in a global ranking assessing support systems and the digital environment for entrepreneurs. Additionally, it ranks 126th out of 141 countries in the Ease of Doing Business Index, indicating the need for improved technology governance and the transformation of obsolete business practices.
However, the COVID-19 pandemic’s new realities have served as a blessing in disguise, driving the world to engage extensively online and demonstrating the criticality of technology adoption for survival in this transformed landscape. SMEs, leading the charge in adopting technology, have reaped the benefits of sustainable business practices and more efficient capital management.
After the pandemic, SMEs have already embraced basic technology solutions such as personalized content engines and survey tools to maintain customer engagement. Many SMEs have shifted their business model online, capitalizing on home delivery and digital payment options. Nevertheless, to explore the full market potential, SMEs need more than traditional tier-one ICT solutions. In today’s digital era, services like hosting, storage, website creation tools, cyber security, and IoT become indispensable for small businesses right from the start.
Case studies of the Impact of 4IR on SMEs in Bangladesh:
Case study 1: Adiba Metal Industries is a small business that started as a proprietary organization producing cooking pans with around 25 employees. However, with the expansion of its product line, the owner faced challenges such as theft and inadequate financial data. With the help of a local ICT entrepreneur, the owner installed close-circuit surveillance cameras and accounting and inventory solutions. This adoption of 4IR-based technical solutions helped Adiba Metal Industries overcome its challenges and expand to become a small enterprise with 67 employees. This case highlights the importance of adopting advanced cloud-based technology in business operations, even for small enterprises, to improve efficiency and facilitate growth.
Case Study 2: Shashya Prabartana is an agro and processed food industry business that supports ecological agriculture and produces safe and nutritious grocery products. They adopted their own e-commerce system in 2020 and hired their own delivery men, which helped them reach more customers and increase sales volume. The company directly sells their products to customers through their website, and they use inventory management software to ensure product availability. Despite challenges in website development and maintenance, the company was able to overcome these hurdles by hiring a skilled employee to maintain their social media and website. The owner of the business notes that online sales were higher during the pandemic than during regular times, and the company has now opened an offline shop in Banani. Usage of the Internet has made their business more profitable.
Technology adoption by SMEs
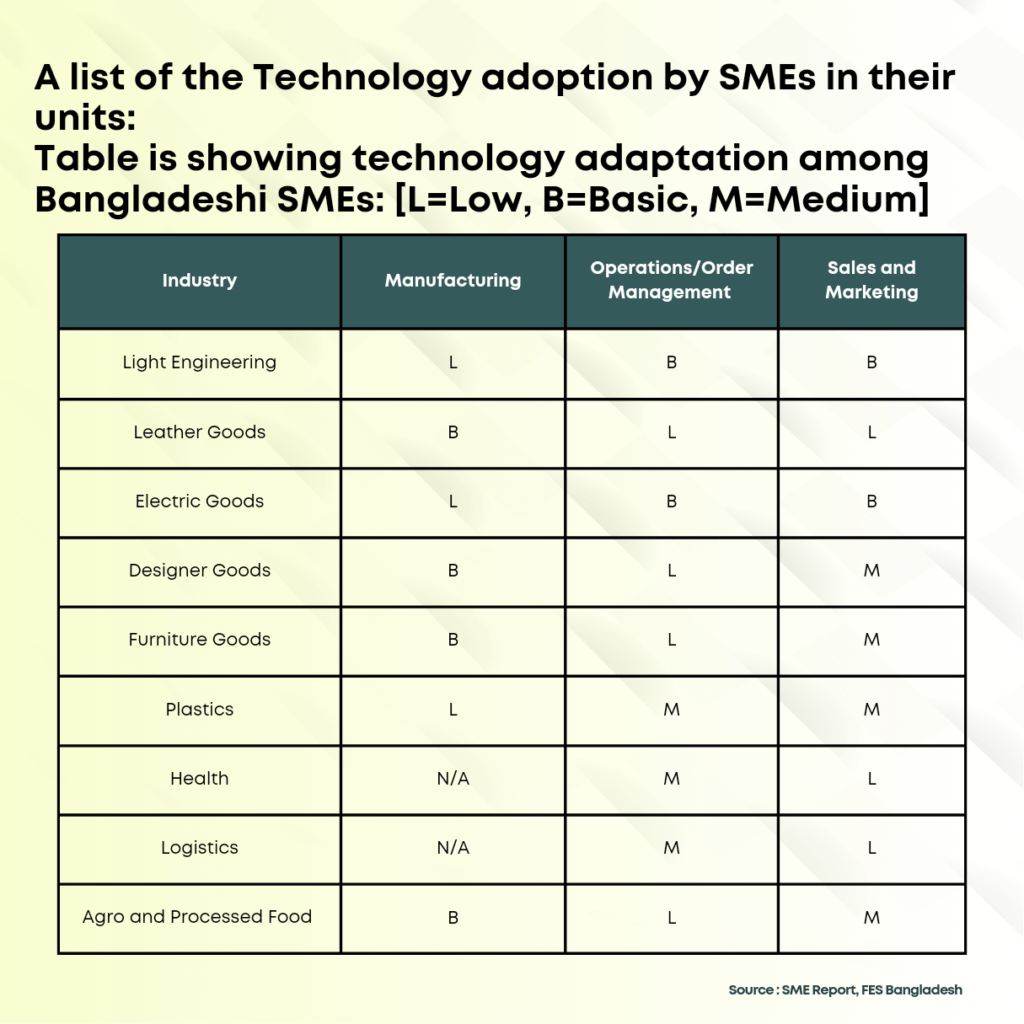
The SME sector in Bangladesh is one of the essential areas for providing employment. In recent times, SMEs have been accepting technologies to boost their businesses. Several Bangladeshi tech companies are catering to the SME sector of the country. They provide ERP, digital marketing, full-stack B2B solutions, operations, logistics, raw materials, accounting solutions, etc. Although most of the SMEs are yet to adopt technologies to boost businesses. Following is a list of the Technology adoption by SMEs in their units:
4IR’s Challenges and Opportunities for Employment
The 4th Industrial Revolution in Bangladesh has resulted in enhanced manufacturing sector productivity and opened up fresh prospects for entrepreneurs. However, it has also posed challenges like growing inequality and job displacement due to automation. To ensure inclusive benefits from the 4th Industrial Revolution, the government is actively implementing programs like Skill Development for Industry 4.0.
Challenge : Automation taking over 5 major industries
A recent study commissioned by a2i, projects that 47% of employment in Bangladesh will be at risk by 2041 in five industries, including RMG, which currently account for 81% of Bangladesh’s exports. Around 40% of jobs in sectors such as RMG, Textile, Agrofood, Furniture, Tourism & Hospitality, and Leather & Footwear are at high risk of automation in the next decades. However, the extent of automation vulnerability varies significantly across these industries. Among the 5 sectors, Tourism has the lowest proportion of jobs facing a high probability of automation (20%), while the Furniture & RMG sector has the highest (60%). The Leather & Footwear and Agro-food sectors have 35%-40% risk. In contrast to the potential loss of 5.5 million jobs due to automation and 4IR, the same technological revolution has the potential to create 10 million new positions.
Opportunities: Enhanced Efficiency, More Innovation & Sustainable Practices for SMEs
The 4th Industrial Revolution (4IR) presents a myriad of opportunities for SMEs including enhanced efficiency, global market access, and improved customer engagement. By harnessing technologies like AI, IoT, and data analytics, SMEs can drive innovation and make informed, data-driven decisions. Moreover, the 4IR facilitates a broader scope for innovation, allowing SMEs to easily align themselves with sustainable practices and qualify for benefits provided by the government under the green economy category.
Additionally , A2i Future of Work Lab is coordinating the process of developing a collective intelligence system that uses data and insights gleaned from hundreds of public and private skills service providers, 40+ industry associations, job seekers, as well as 32 government departments under 23 ministries and agencies, to address these challenges and give workers, businesses, and the government an accurate understanding of the current facts and important future trends.
Government’s Initiative towards fostering 4IR :

The GoB is focusing on 3 issues to prepare for the 4IR:
- The development of the industry through the innovation of sophisticated technology
- The creation of a Skilled Workforce
- The Protection of the Environment
Despite the challenges, Impressive strides have been made in Bangladesh’s digital transformation, due to the active engagement of both the government and the private sector at the micro-level of international trade. The adoption of blockchain-based supply chain finance, exemplified by the recent transaction, has significantly reduced LC processing time and streamlined operations. Additionally, the launch of the Orjon blockchain-based digital supply chain finance platform by IPDC in Southeast Asia, with support from DFID and IBM, marks a positive step towards benefiting MSMEs with easier access to loans at a lower cost, while also reducing operational and monitoring expenses for IPDC. However, despite these encouraging advancements, there is still untapped potential in leveraging technologies like Blockchain and Big data analytics in daily business operations. Ensuring accessibility of these technologies to small businesses can enhance the export readiness of products and enrich their business practices, enabling them to make informed, data-driven decisions.




